Issues
The Issues tab shows all code health issues detected in the default branch of your repository.
Browsing issues
The Issues tab lists all code health issues currently detected in the default branch of your repository.
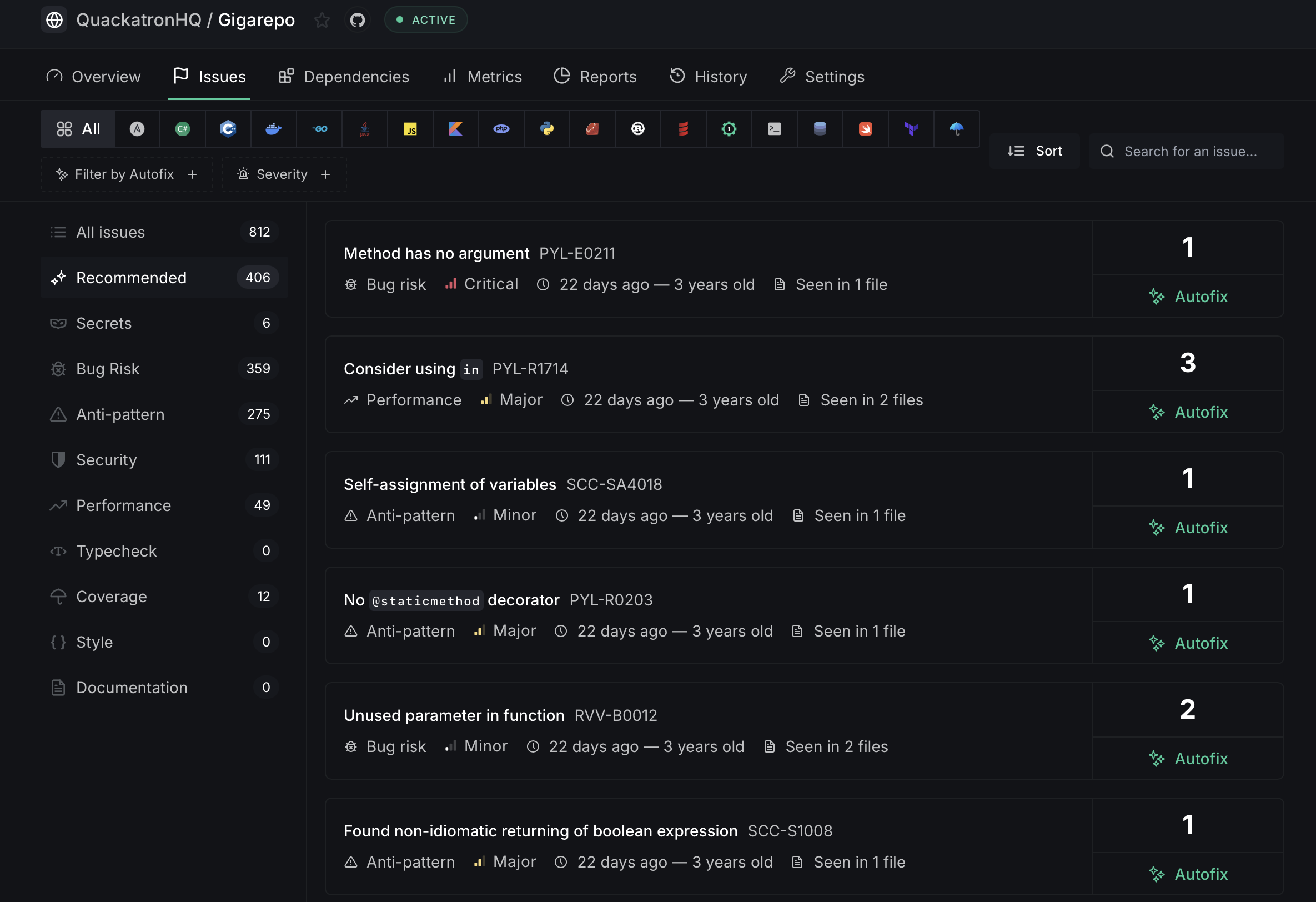
On the left sidebar, issues are grouped by category with counts:
- All Issues — Total number of detected issues
- Recommended — The most critical issues that need immediate attention
- Secrets — Hardcoded secrets and credentials
- Bug Risk — Code patterns likely to cause bugs
- Anti-pattern — Known bad coding practices
- Security — Potential security vulnerabilities
- Performance — Issues affecting runtime performance
- Typecheck — Type-related issues
- Coverage — Code coverage gaps
- Style — Code style violations
- Documentation — Missing or incomplete documentation
Issues with available Autofix™ are marked with an Autofix button on the right.
Filtering and sorting
Use the filter bar at the top to narrow down issues:
- Filter by Autofix — Show only issues that have an Autofix available
- Severity — Filter by Critical, Major, or Minor severity
- Sort — Order issues by most frequent, least frequent, first seen, or last seen
- Search — Find specific issues by title or issue code
Issue detail page
Click on any issue to view its detail page, which shows all occurrences of that issue in your codebase along with contextual code snippets.
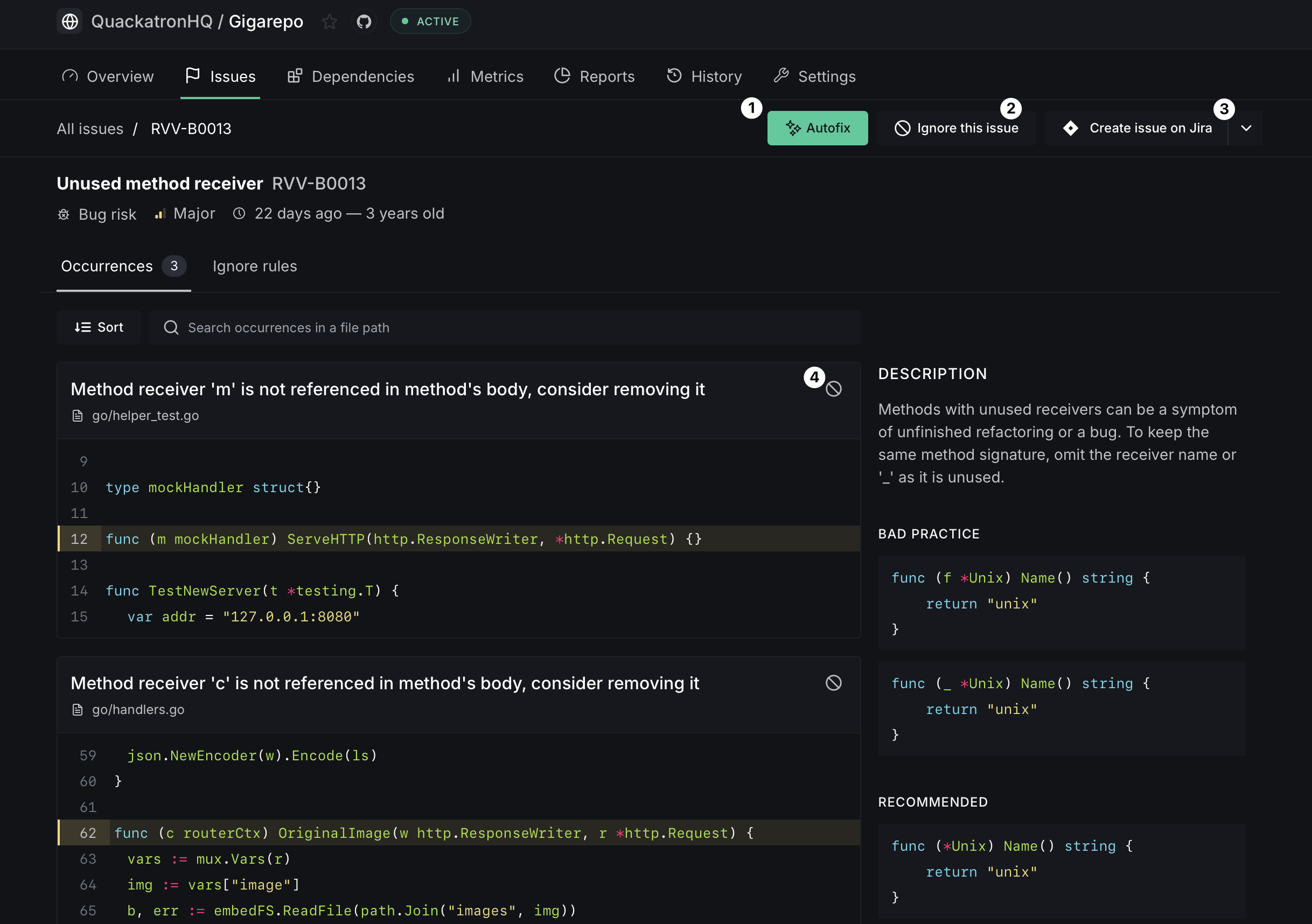
The issue detail page includes:
- Autofix button — Generate automatic fixes for this issue across all affected files
- Ignore this issue — Suppress the issue at various scopes (see Ignoring issues)
- Create issue on Provider — Create a linked provider (GitHub, GitLab or Jira) ticket for tracking
Ignoring issues
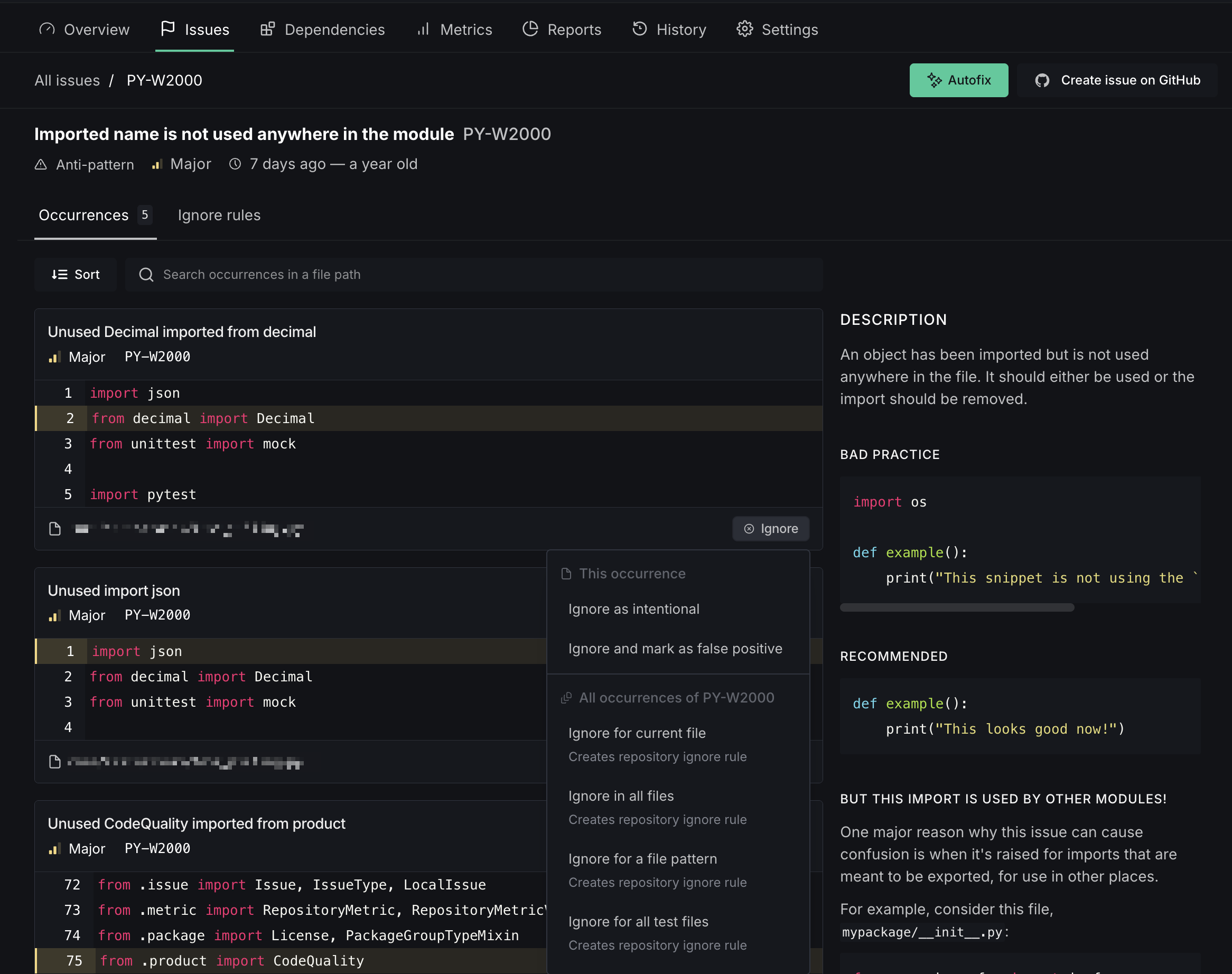
The ignore dropdown lets you suppress issues at several levels:
- For a file pattern — Ignore the issue for files matching a glob pattern (e.g.,
contrib/utils/*.py) - For all test files — Ignore the issue in files matching your configured test patterns
- For all files — Ignore the issue repository-wide in future analyses
False-positives
If you believe an issue is incorrectly flagged, you can mark it as a false positive directly from the ignore dropdown on any occurrence.
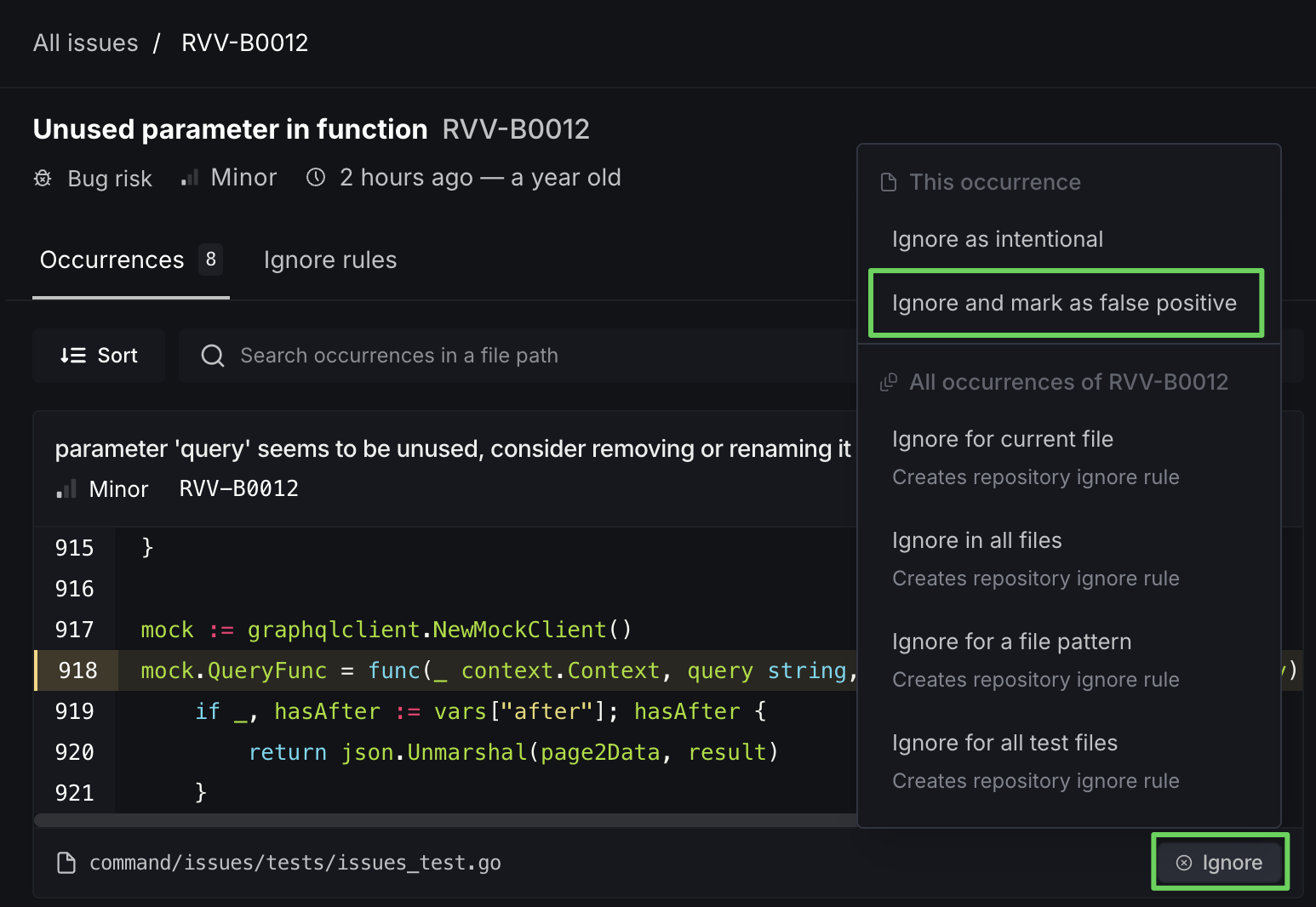
To report a false positive, click Ignore on the occurrence and select Ignore and mark as false positive.
When you mark an occurrence as a false positive:
- The occurrence is suppressed and will no longer appear in your issue count
- A report is sent to the DeepSource engineering team so they can review and improve analyzer accuracy
- The ignore rule applies only to that specific occurrence — other occurrences of the same issue are unaffected
Autofix
Issues that support Autofix show an Autofix button on both the issue list and the issue detail page. Clicking it tells DeepSource to generate fixes for all occurrences of that issue.
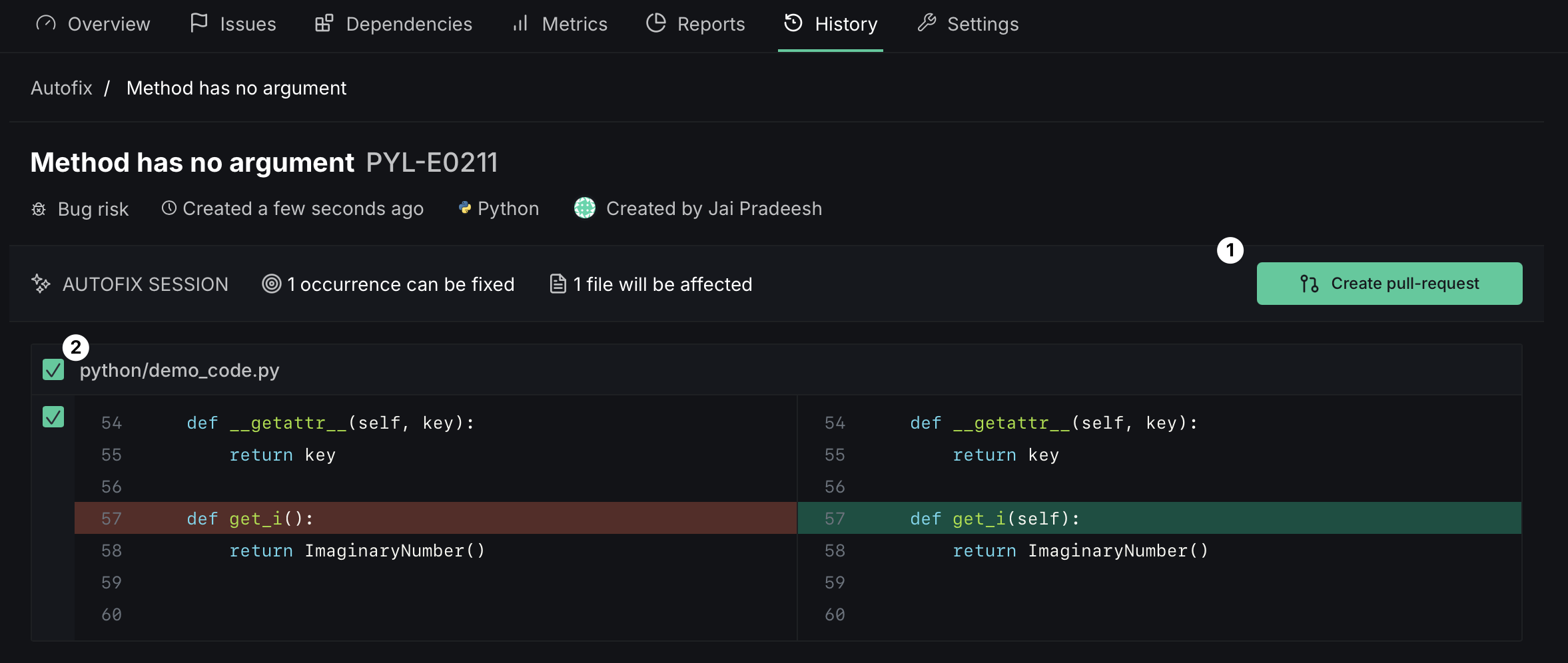
Once the fixes are ready, you can review the proposed changes and apply them:
- Create pull request — when Autofix is triggered from a default-branch analysis, the fixes are submitted as a new PR
- Commit to pull request — when triggered from an existing PR's analysis, the fixes are committed directly onto that PR's branch
Silencing issues in code
You can permanently silence issues using the skipcq keyword in your source code.
Silencing a specific issue
Add skipcq: as a comment with the issue's short-code at the end of the line, or on the line above it:
input = 10 # skipcq: PYL-W0622# skipcq: PYL-W0622
input = 10Silencing multiple issues
Add a comma-separated list of issue short-codes after skipcq::
def function(input, an_argument_not_used): # skipcq: PYL-W0622, PYL-W0613
passSilencing all issues on a line
Use skipcq without any issue codes to silence all issues on a line:
except Exception: # skipcq
passThis prevents all issues from being raised on this line. We recommend specifying the exact issue codes to be suppressed.
In conjunction with existing comments
Add skipcq at the end of an existing comment, or place the skipcq comment on a separate line above:
class Klass:
def __init__(self):
pass
# skipcq
# This function does not use `self`.
def func(self, x):
return x ** 2Universality
The skipcq keyword works across all languages and analyzers. The general format is:
a line of code <comment identifier> skipcq: <issue code 1>, <issue code 2>For example, in Go:
y := !!y // skipcq: SSC-SA4010