Settings
The repository settings page lets you configure how DeepSource analyzes your code, manages quality gates, and integrates with your workflow. You can access it from the Settings tab on any repository page.
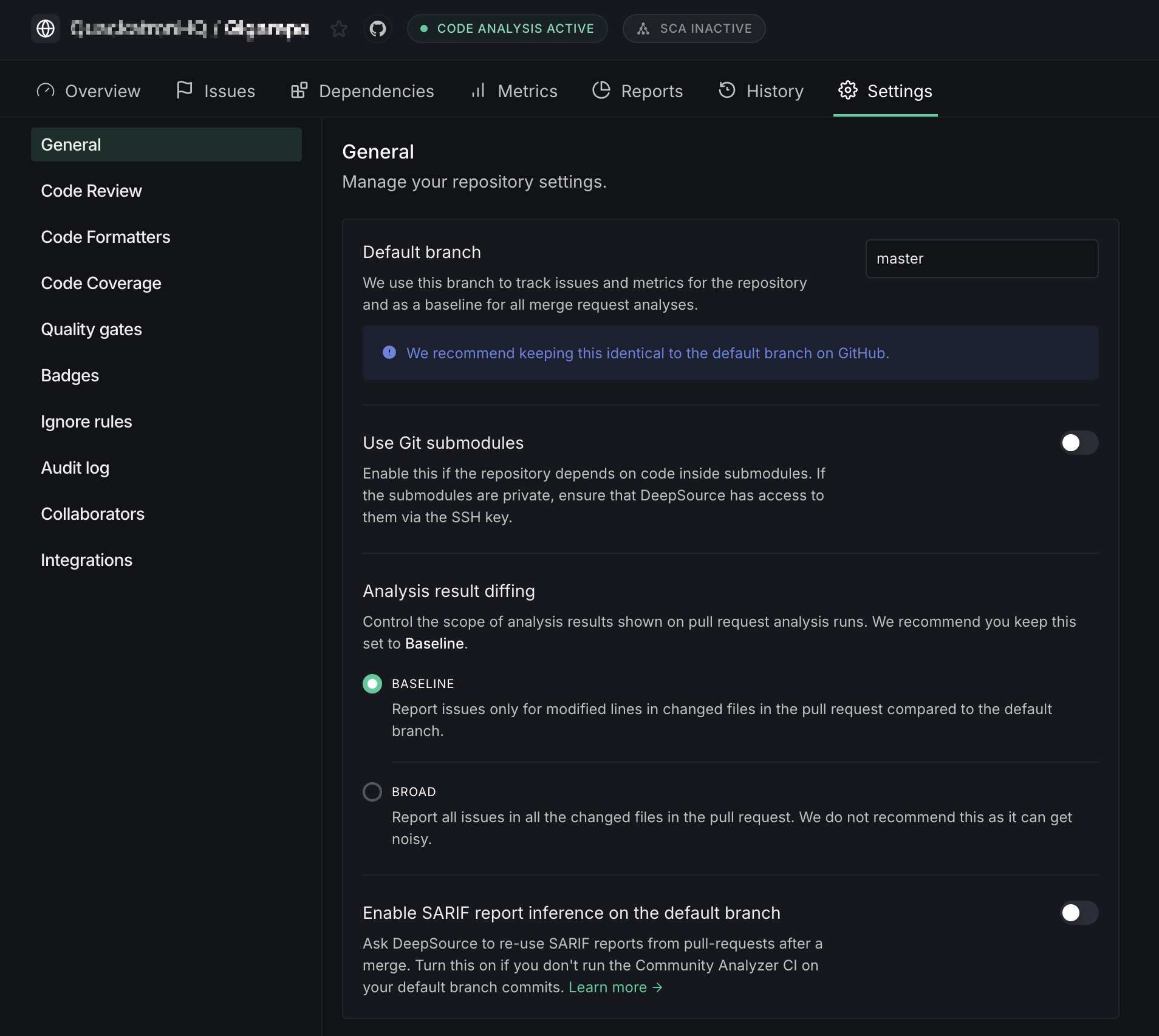
General
Manage your repository's core analysis settings.
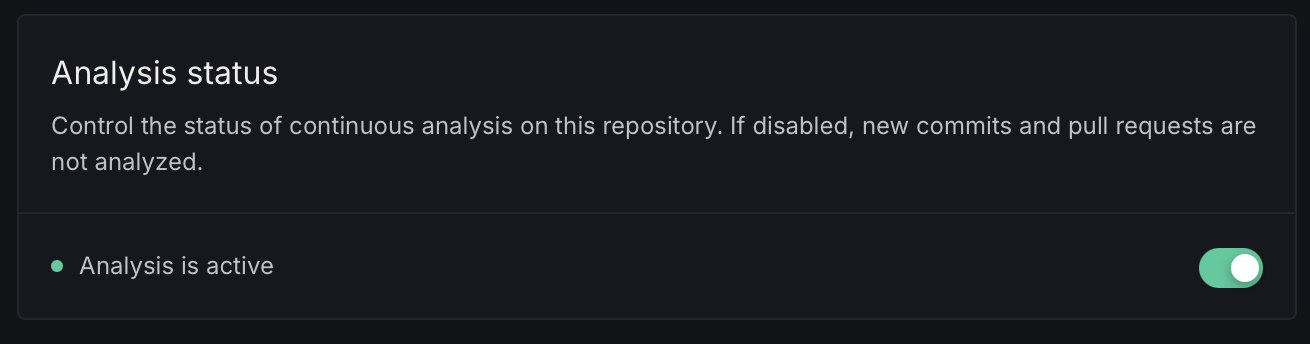
Analysis status
Control whether continuous analysis is active on this repository. When disabled, new commits and pull requests are not analyzed.
Default branch
Set the base branch for analysis by DeepSource. Your issues tab will be populated with the issues found on this branch.
Use Git submodules
Enable this if your repository relies on code within submodules. If these submodules are private, ensure that DeepSource can access them using the SSH key as documented in the SSH access section below.
Analysis result diffing
Control the scope of analysis results shown on pull request analysis runs.
- Baseline: Report issues only for modified lines in changed files in the pull request compared to the default branch
- Broad: Report all issues in all changed files in the pull request. This can get noisy, and is not recommended
Enable SARIF report inference on the default branch
Ask DeepSource to re-use SARIF reports from pull requests after a merge. Turn this on if you don't run the Community Analyzer CI on your default branch commits.
Code Review
Configure the settings for code quality and security review. You can enable as many analyzers you need and adjust individual properties for each to suit your development environment.
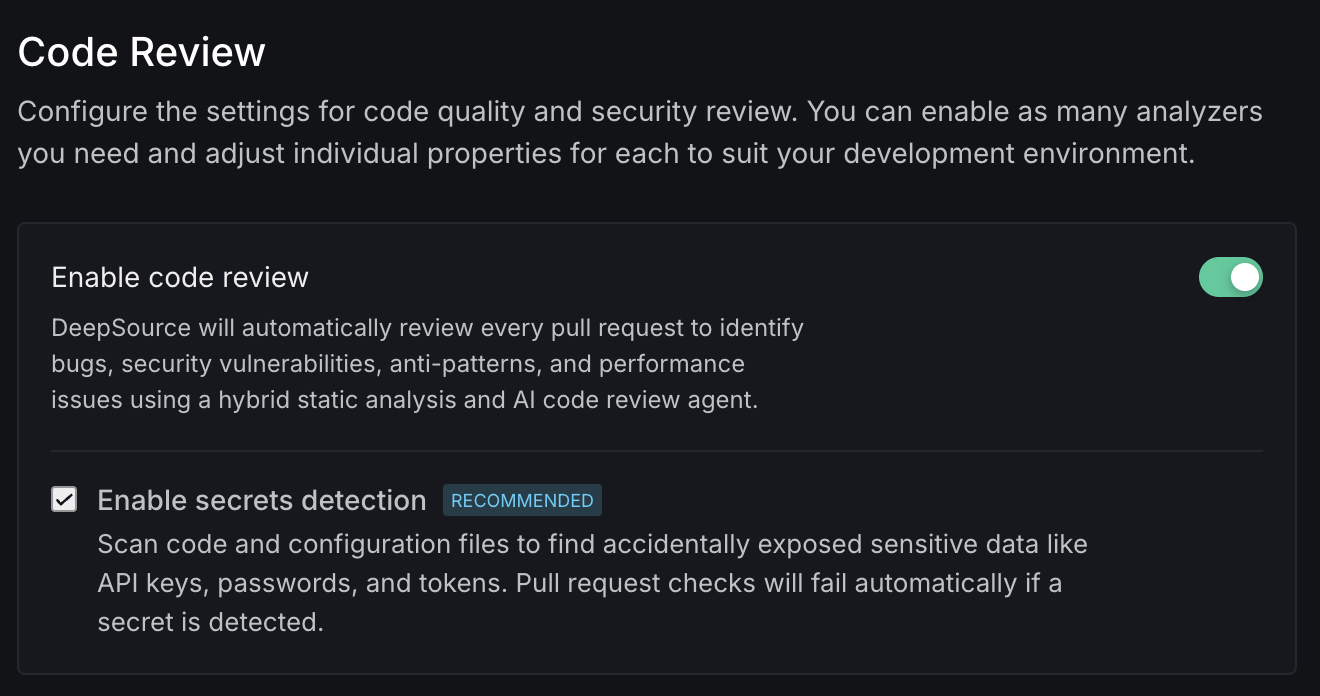
Enable code review
DeepSource automatically reviews every pull request to identify bugs, security vulnerabilities, anti-patterns, and performance issues using a hybrid static analysis and AI code review agent. Use the toggle to enable or disable automatic code review for your repository.
Enable secrets detection
This setting is recommended for all repositories.
Scan code and configuration files to find accidentally exposed sensitive data like API keys, passwords, and tokens. Pull request checks will fail automatically if a secret is detected.
For more details on how detection works, see Secrets Detection.
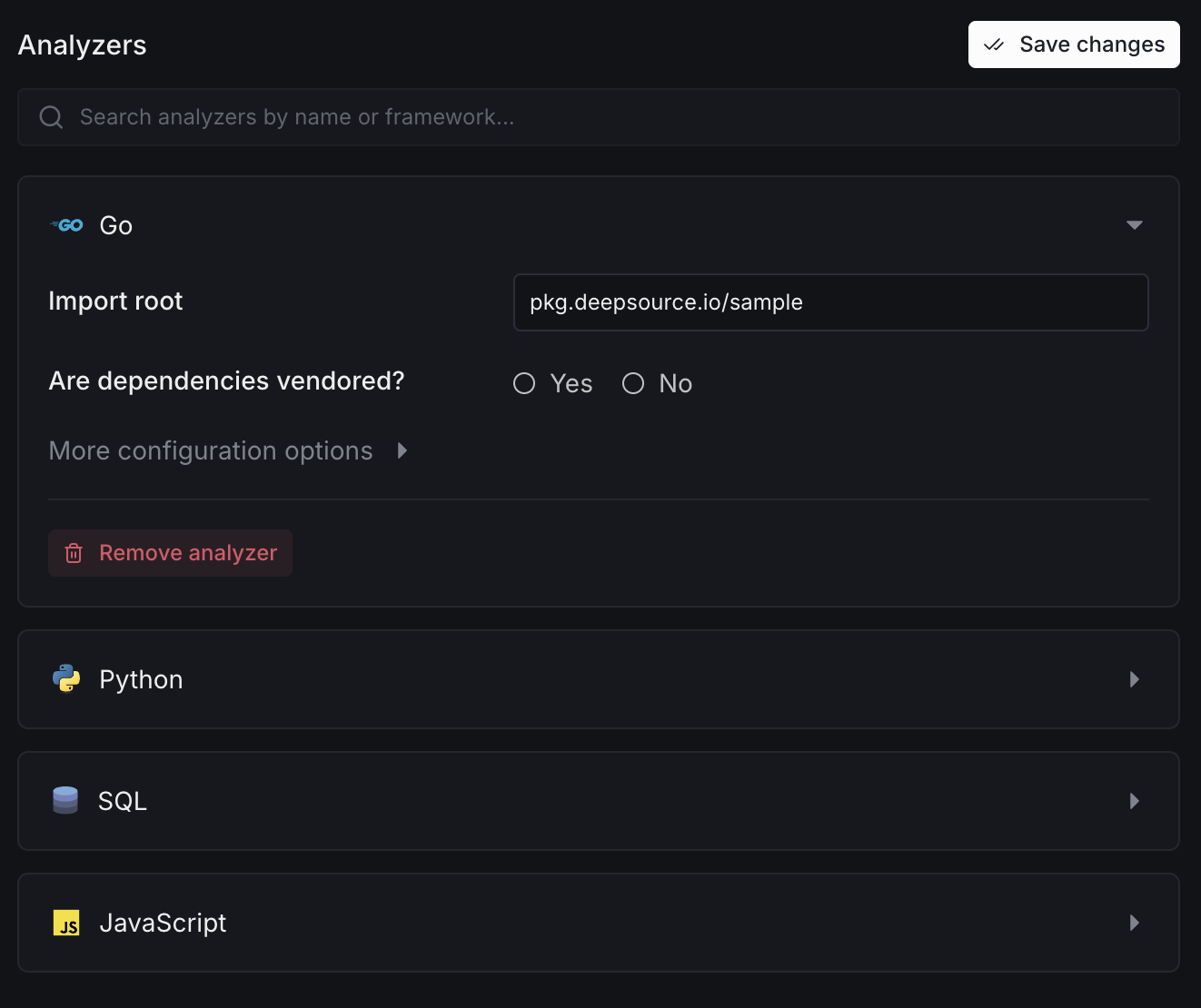
Analyzers
Search and configure the analyzers enabled for your repository. Each analyzer can be expanded to view its language-specific settings like import root and dependency vendoring options.
Codebase Context
Define glob patterns that help DeepSource understand your codebase and reduce false positives.
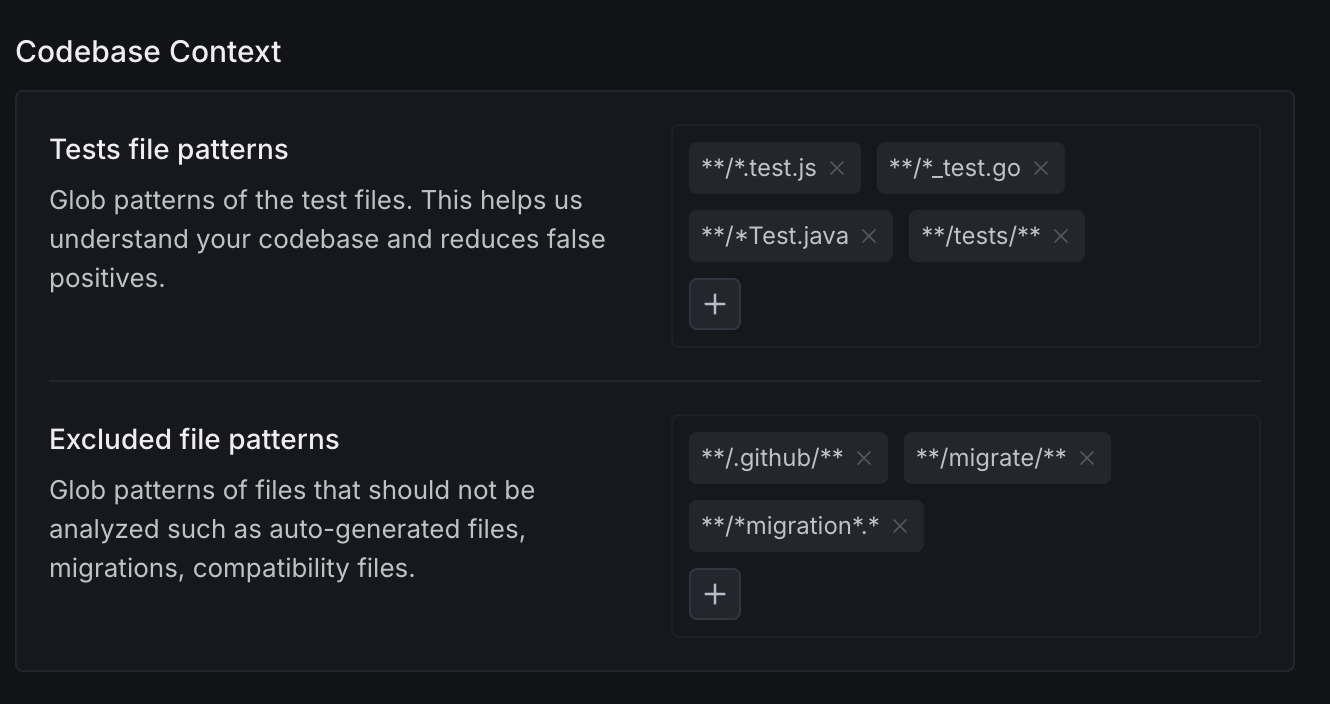
- Tests file patterns: Glob patterns of your test files (e.g.
**/*.test.js,**/*_test.go). This helps DeepSource understand your codebase and reduces false positives. - Excluded file patterns: Glob patterns of files that should not be analyzed, such as auto-generated files, migrations, or compatibility files (e.g.
**/.github/**,**/*migration*.*).
Code Formatters
Automated code formatting that doesn't break your build. When enabled, DeepSource runs code formatters on every commit on every pull request. If the code needs formatting, it'll automatically add a new commit with the changes on top of the last commit.
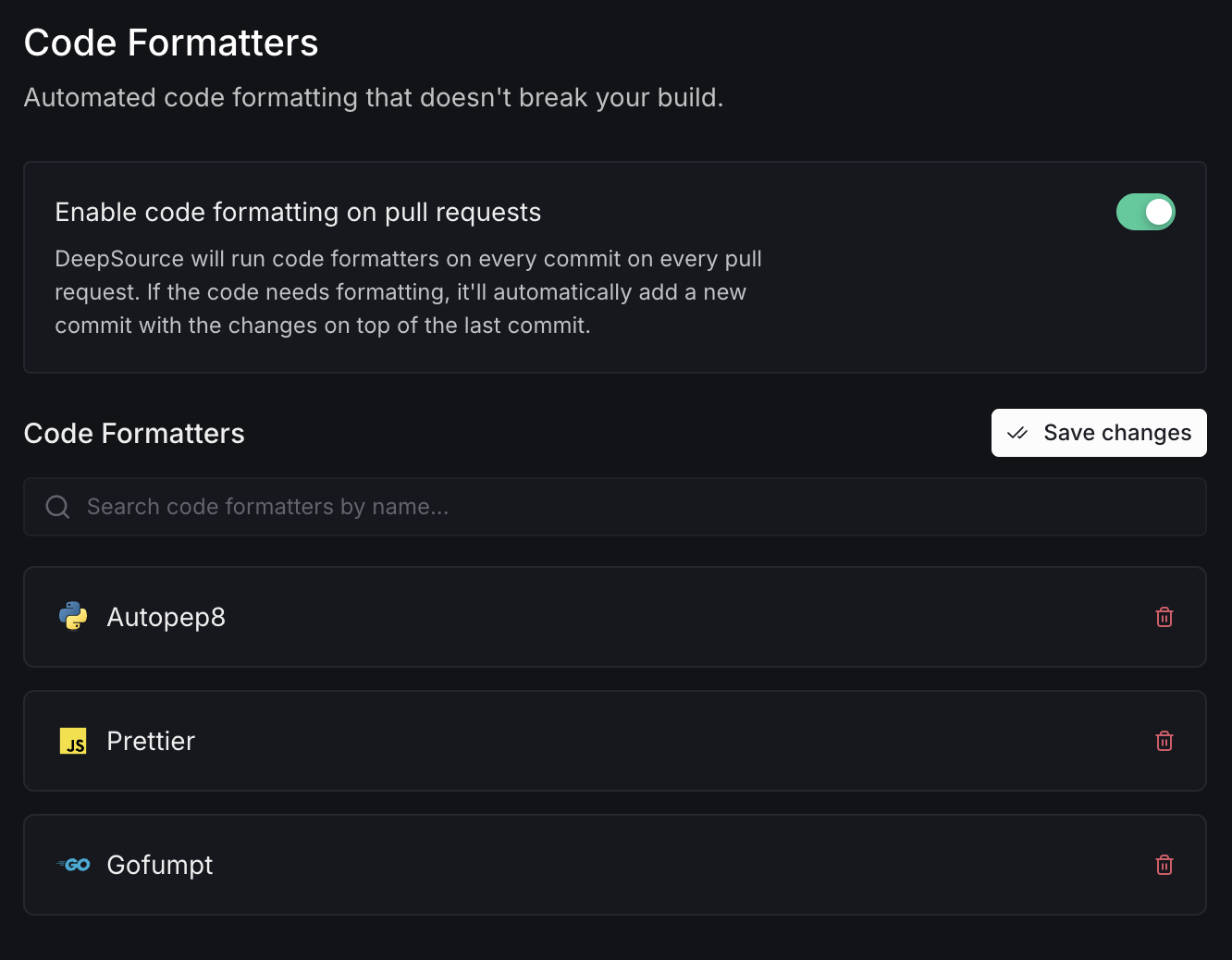
You can search and manage the code formatters enabled for your repository.
Code Coverage
On this page, you can manage how you track the code coverage of a repository.
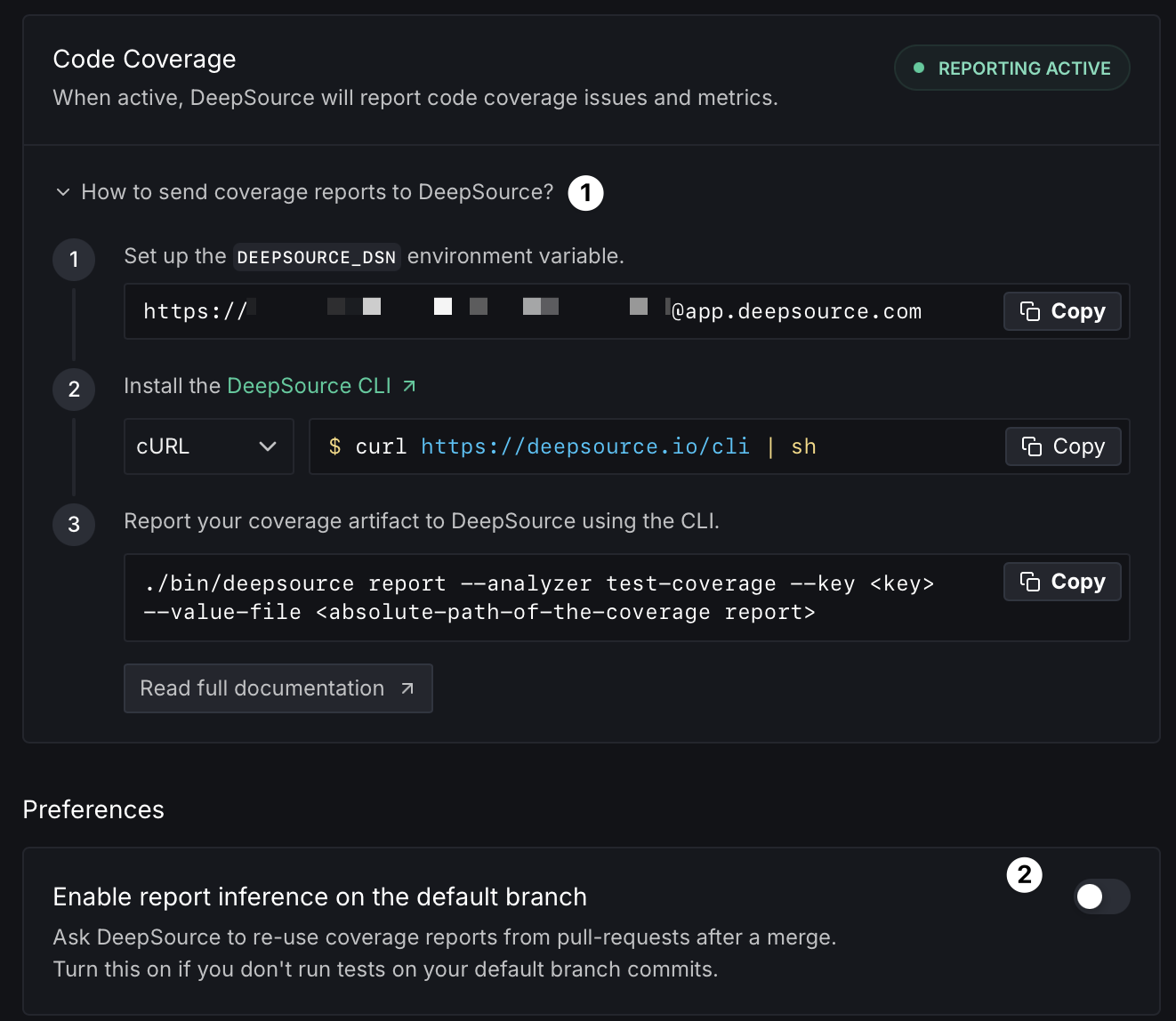
Enable Code Coverage tracking
Refer to the Track code coverage guide for steps on how to setup code coverage on a repository.
Enable report inference on the default branch
A common way developers setup CI on their repositories is to run the full test suite on pull requests and avoid running the same tests on the merge commits for when pull requests get merged to the default branch. In such a case, DeepSource's Test Coverage analyzer may fail on commits to the default branch as no coverage report would be received for analysis.
To allow such use-cases, DeepSource provides an option to re-use coverage reports from pull requests after a merge. By enabling this option, on merge commits to the default branch, the Test Coverage analyzer will re-use the coverage reports from the last analysis on the related pull request.
Quality Gates
Configure quality gates for your repository.
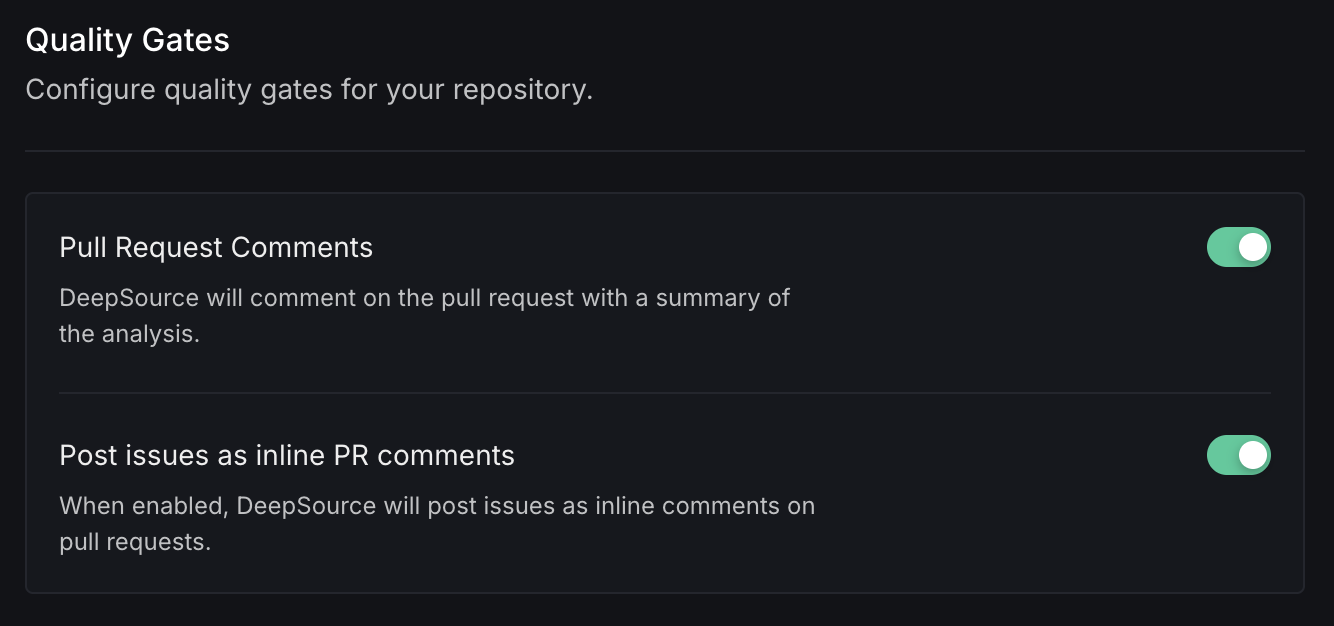
Pull Request Comments
DeepSource will comment on the pull request with a summary of the analysis. This makes understanding and auditing code health problems in the code review flow easier without navigating away from the pull request.
Post issues as inline PR comments
When enabled, DeepSource will post issues as inline comments on pull requests, highlighting the exact lines where issues were detected.
Issue Reporting
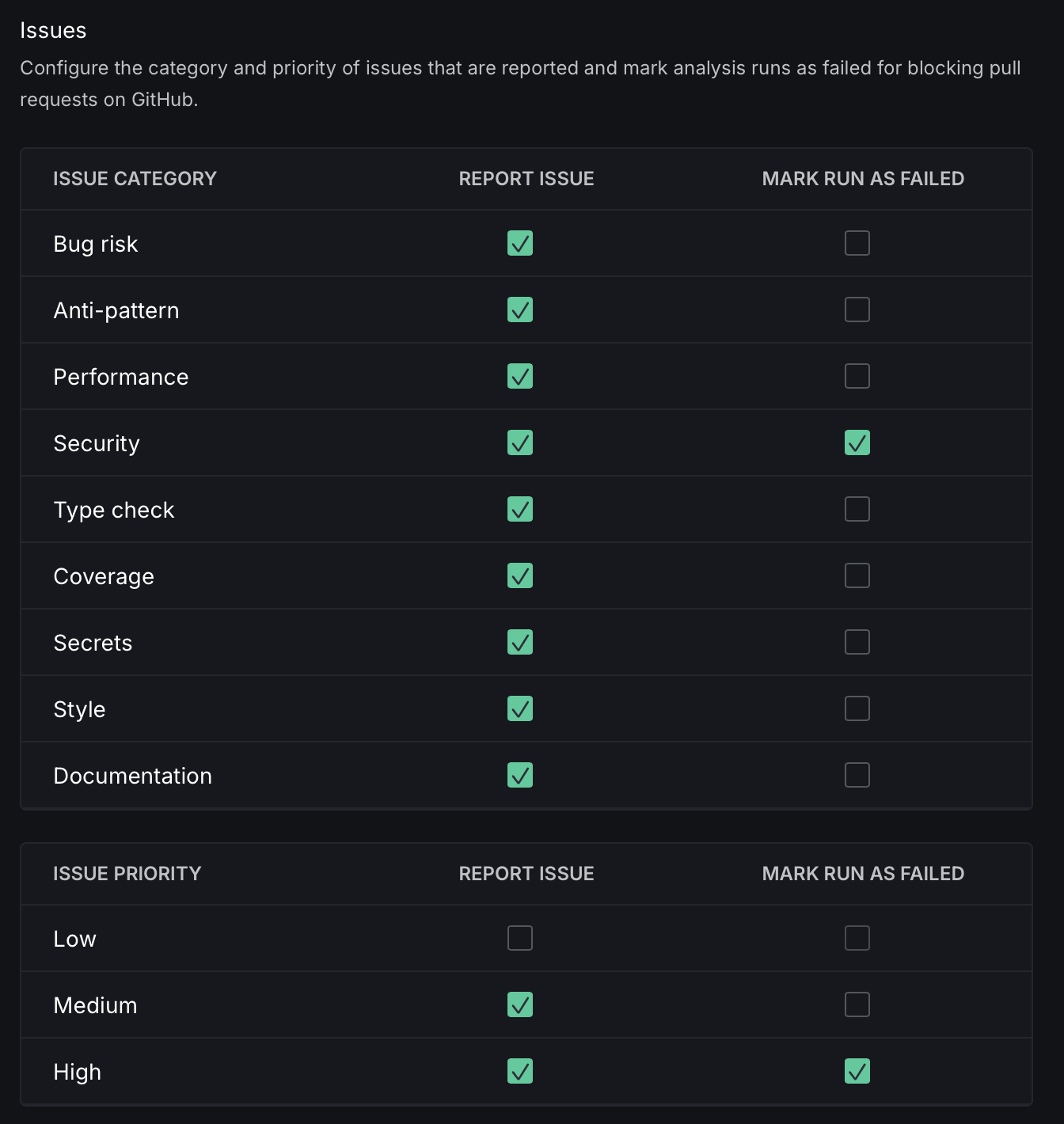
Customize the reporting of issues by selecting the categories and severities to include and setting the criteria for failure.
You can filter issues by category (anti-pattern, bug risk, coverage, documentation, performance, security, style, type check) and by severity (critical, major, minor). Both filters apply to repo-level and group-level quality gates, letting you control exactly which issues cause a run to fail.
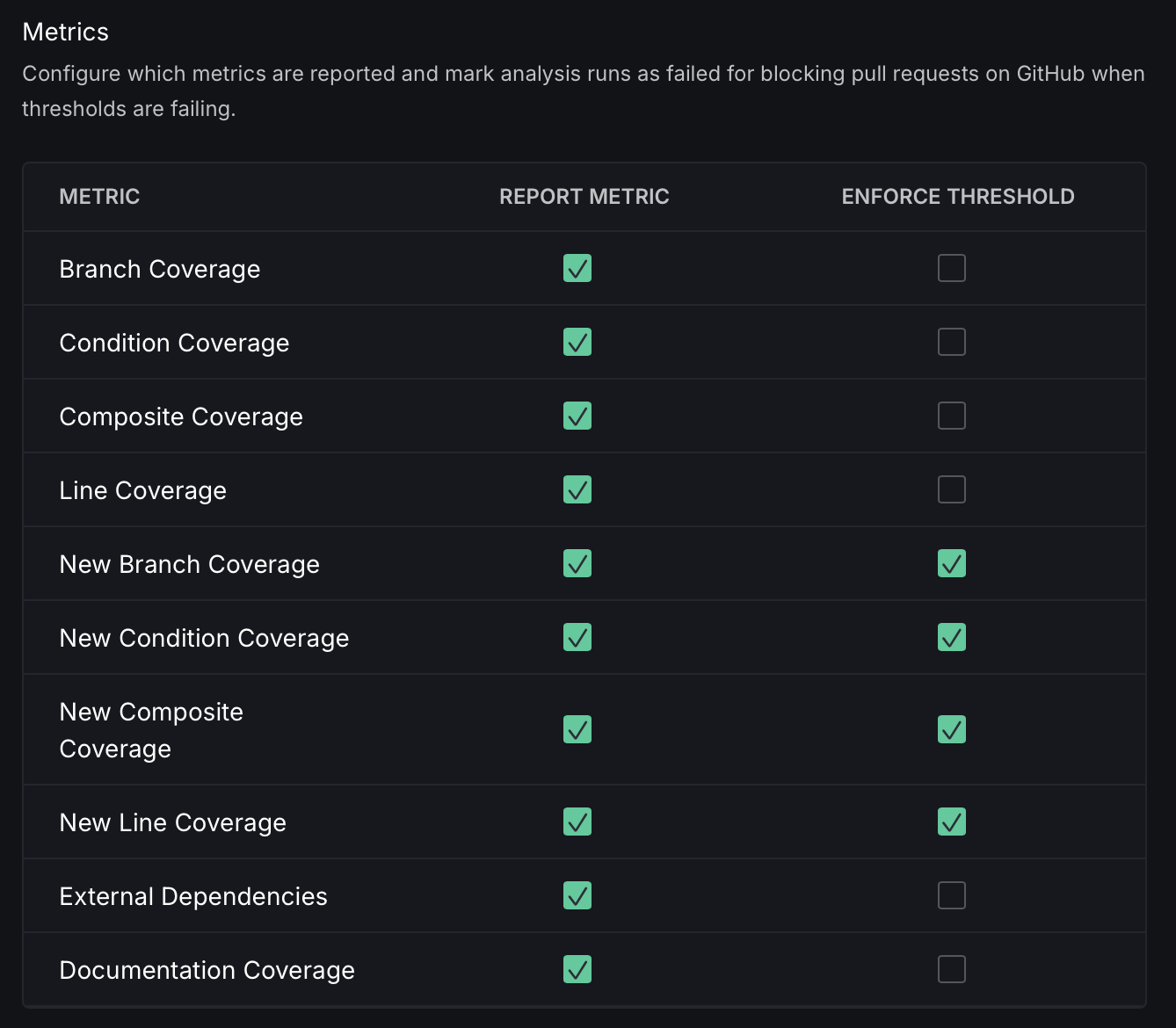
Metrics Reporting
Customize metrics reporting by selecting the metrics to be included and setting thresholds for failure. Analysis runs will be marked as failed if these thresholds are not met.
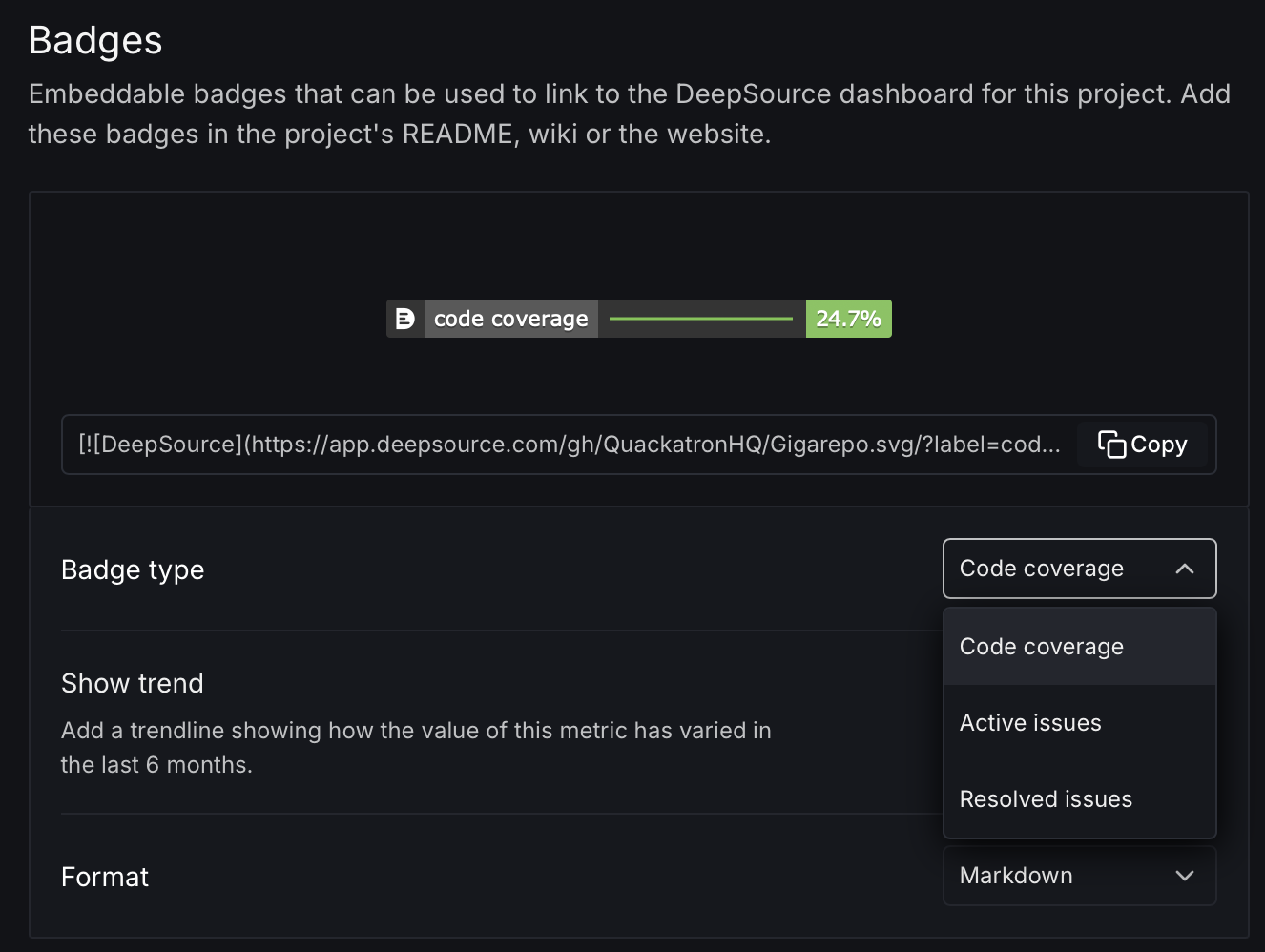
Badges
You can add embeddable badges with data on the number of active issues, resolved issues and code coverage in this repository to your project's README, wiki, or website. These badges can be formatted in Markdown, AsciiDoc, HTML, or reStructuredText.
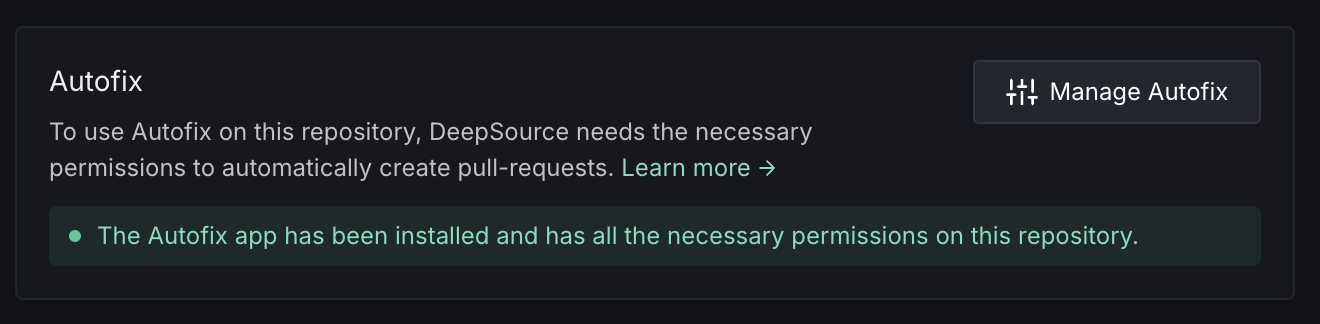
Autofix™
To use Autofix on this repository, DeepSource needs the necessary permissions to automatically create pull requests.
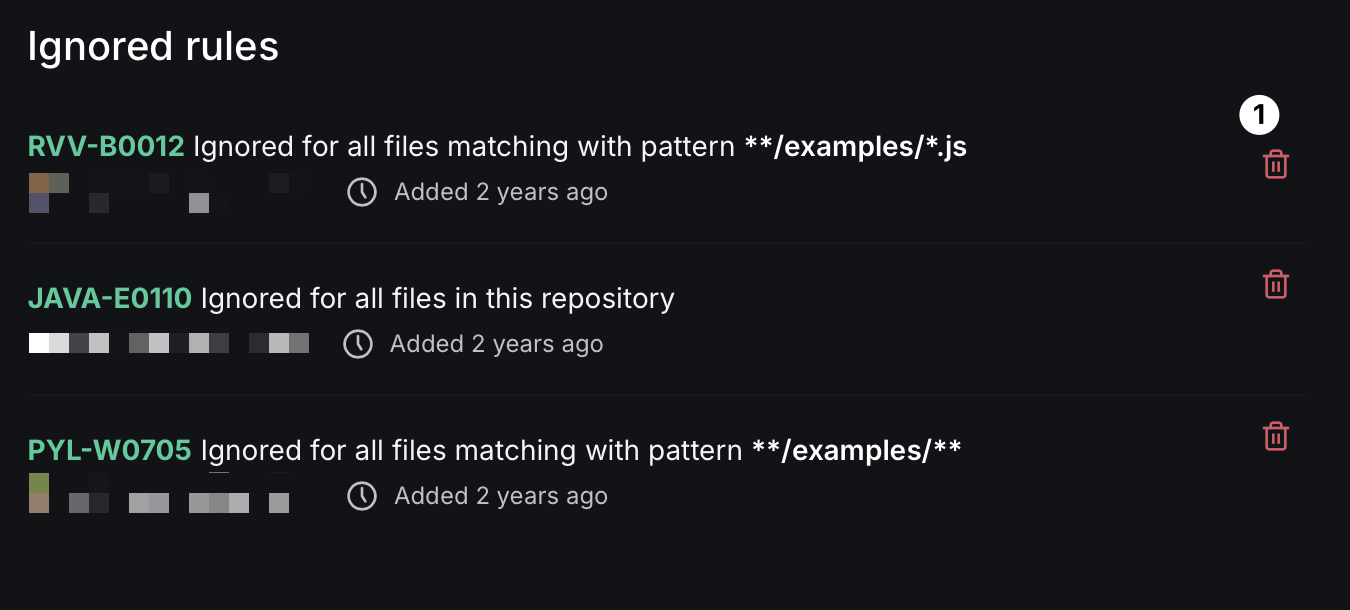
Ignore rules
In this section, you'll find all the ignore rules that you have added. To remove an ignore rule, click on the bin icon next to it. Read more about ignoring issues.
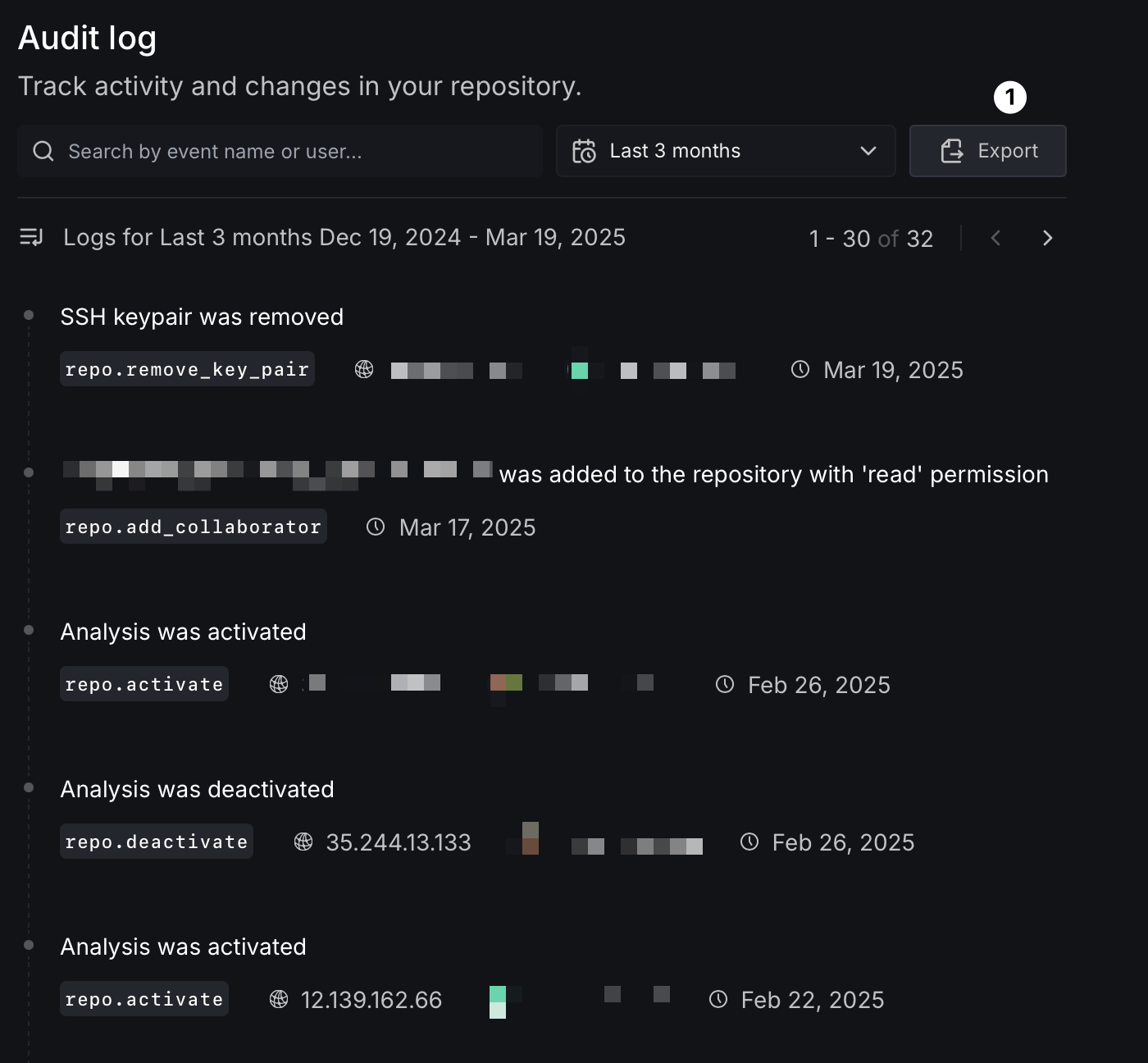
Audit log
The audit log provides a comprehensive record of all events and actions related to the analysis and configuration of your repository on DeepSource. This includes events such as activating or deactivating analysis, creating or deleting ignore rules, adding or removing team members, as well as any other changes made to the configuration or settings of DeepSource within the repository.
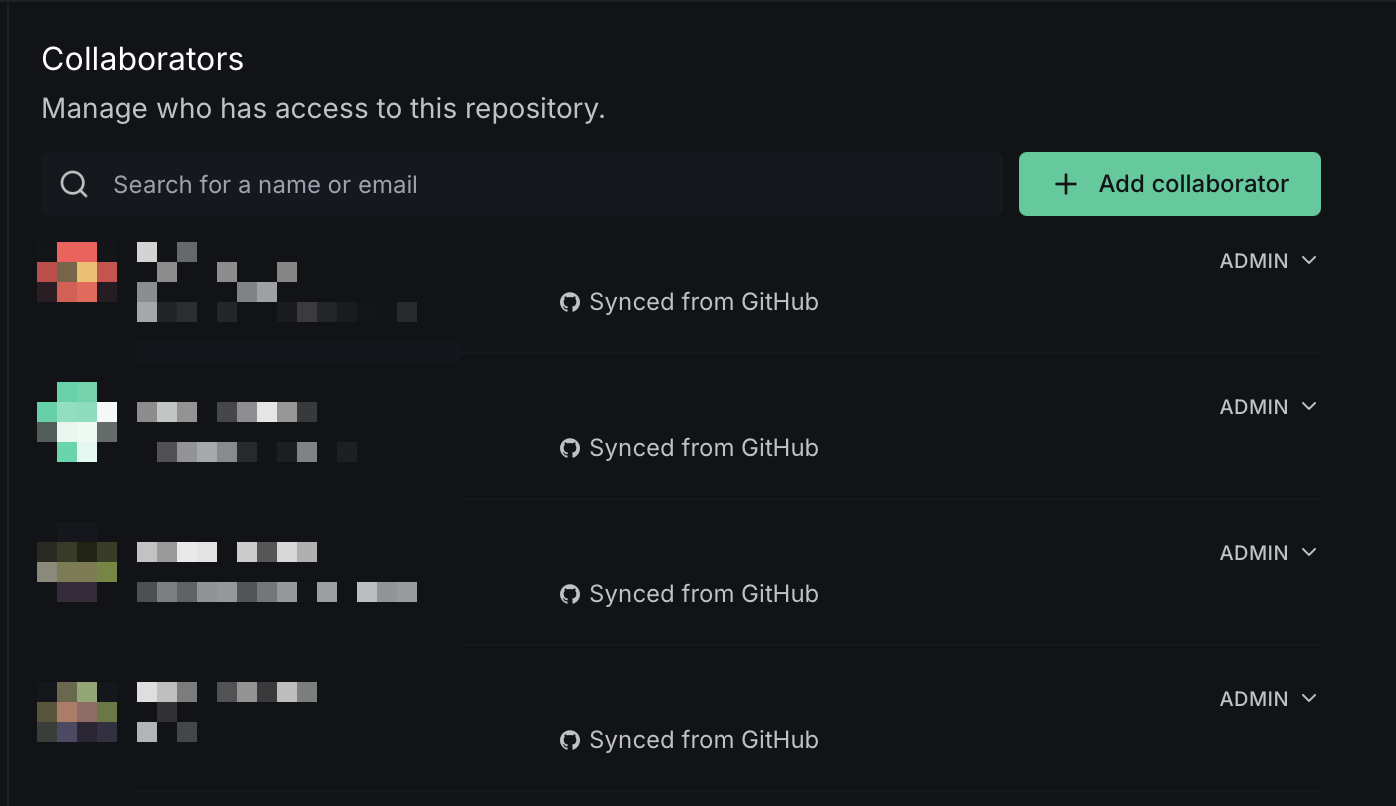
Collaborators
In this section, you can view a list of all members who have access to the repository. To modify a member's access level, click the dropdown and select Admin, Write, or Read-only. If you need to add a new collaborator to the repository, click on the Add Collaborator button.
New collaborators must first be invited to join the team before they can be added as repository members.
Integrations
Connect third-party services to your repository for notifications and issue tracking.
SSH access
If this repository has external private dependencies, grant DeepSource access to fetch those dependencies via a public key.
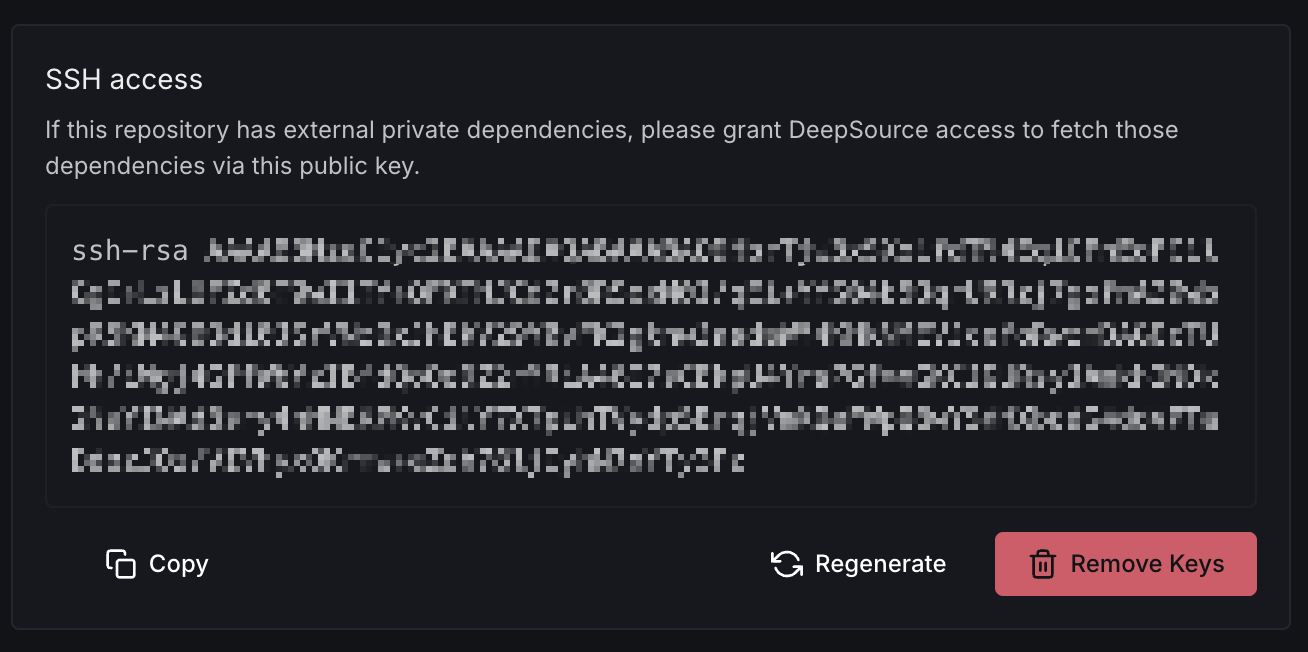
Once a key pair is generated, copy the public key and add it as a deploy key in the dependency or submodule repository. You can choose to copy, regenerate, or remove the key as needed.
If you have multiple submodules, you must add the generated SSH key to all submodules. In case of GitHub, this won't work — it would complain that this key is in use elsewhere. To fix this, create a machine user, add the generated SSH key for that user, and give this machine user access to all your submodule repositories.
Data Source Name (DSN)
Use the DSN to send external information about this repository to DeepSource from external sources, such as DeepSource CLI. Keep this confidential.
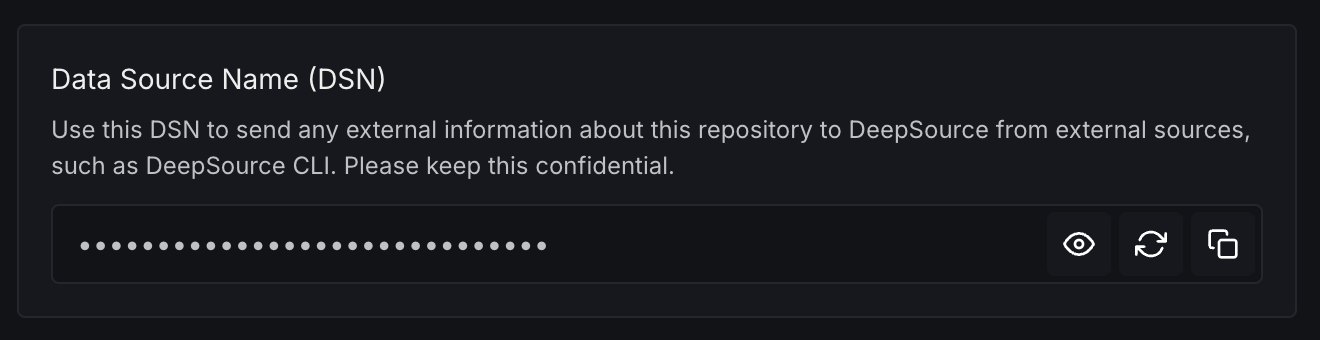
You can view, copy, or regenerate the DSN. Regenerating the DSN will invalidate the old one, so be sure to replace it with the new one wherever it is being used.